HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY MAINTENANCE 30
|
|
|
- Melvyn Beasley
- 8 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Curriculum Development In the Fairfield Public Schools FAIRFIELD PUBLIC SCHOOLS FAIRFIELD, CONNECTICUT HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY MAINTENANCE 30 Board of Education Approved 05/22/2007
2 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY MAINTENANCE 30 Statement of Purpose Science education promotes essential understandings of the natural world and nurtures students abilities to apply scientific knowledge to make informed and logical judgments about personal and societal issues. As such, this education requires that the fundamental approach to science be a creative and logical process for investigating, reasoning, critiquing and communicating about ideas, not just a static body of facts to be memorized. Understanding the interconnections between science and technology and their shared impact on the environment and societal issues is essential for all students. This elective course provides an introductory treatment of the structure and function of the human body for students who have already completed a first course in general biology. This knowledge is critical for students when making personal decisions that affect their health and the health of their families. Audience Grade 11 and 12 Prerequisite Successful completion of four (4) credits of science including Biology. Design and Description This second-year course in biology emphasizes the workings of the human body. The course is offered in the spring semester and meets six (6) periods per week including one double lab period. This course provides an introductory treatment of the structure and function of the human body for the following topics: anatomical terminology, metabolism and nutrition, the digestive and respiratory systems, the cardiovascular and immune systems, and the excretory system. Each topic is approached from simple to increasingly complex levels, where an understanding of concepts is emphasized rather than mere memorization. Students are encouraged to work both independently and in cooperative groups within the lab/classroom with teacher guidance. A major research paper in which students analyze their own diets with regard to established RDA s is required. Course Objectives Students will be able to: trace the pathway of blood throughout the body as it passes through the four chambers of the human heart. identify the heart valves and describe their location, function, and mechanism of operation. trace the conduction pathway of the heart and describe the events of cardiac muscle contraction that results. outline the timing and events of the cardiac cycle (systole and diastole). compare and contrast the structure and function of arteries, veins, and capillaries. define vasoconstriction and vasodilation as they regulate blood flow into capillary beds. HAP Maintenance 2
3 identify fetal vascular modifications, or fetal shunts, and describe their function before birth. distinguish cardiovascular-related disorders, including their symptoms, prevention, and control. outline the composition, physical characteristics, and functions of whole blood. differentiate among the functions of each of the formed elements of blood and plasma. differentiate between fetal and adult hemoglobin. relate the basis for a transfusion reaction based upon ABO and Rh blood groups. outline the mechanism of blood-clotting and some factors that may affect clotting time. analyze the importance of blood testing as a diagnostic tool. identify blood-related disorders, including their symptoms, prevention, and control. relate the function of the lymphatic system to the cardiovascular and immune systems. relate the distribution of lymph nodes and vessels to the point of entry of foreign bodies. define the composition of lymph and explain its formation and transport through lymph nodes and lymph organs. summarize the body s three lines of defense against pathogens compare and contrast the development and function of T-lymphocytes and B- lymphocytes. analyze the structure of an antibody in terms of genetic recombination. distinguish between active and passive immunity as well as between natural and artificial immunity. compare immunodeficiencies, allergies, and autoimmune diseases. define the structure and function of each respiratory organ. differentiate among cellular respiration, external respiration, internal respiration, pulmonary ventilation, expiration, and inspiration. trace how the respiratory muscles can cause volume changes that lead to air flow into and out of the lungs. summarize the process of gas exchanges in the lungs and tissues by applying the gas laws. compare and contrast how oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the blood. compare the causes and consequences of chronic bronchitis, emphysema, asthma, and lung cancer. summarize the overall function of the digestive system and differentiate between organs of the alimentary canal and accessory digestive organs. differentiate between mechanical/physical digestion and chemical digestion and where each process occurs in the alimentary canal. outline the general activities of each digestive system organ. differentiate between deciduous and permanent teeth HAP Maintenance 3
4 outline the mechanisms of chewing, swallowing, choking, peristalsis, absorption, vomiting, and defecation. define the composition, origin, and activity of each of the major digestive juices. define the function of the villus in normal and abnormal digestive processes. identify digestion-related disorders, including their symptoms, prevention, and control. identify the six major nutrient categories, noting the important dietary sources, energy content, and principle cellular uses of each. define enzyme, metabolism, anabolism, and catabolism. analyze the importance of energy balance and basal metabolic rate (BMR) Distinguish between fat- and water-soluble vitamins and describe consequences of their deficit or excess. summarize the need for protein synthesis in body cells and the supply of dietary amino acids from complete and incomplete proteins. compare and contrast saturated and unsaturated fatty acids and the consequences of their deficit or excess. differentiate between LDLs and HDLs relative to their structures and major roles in the body. identify the following regions of a longitudinal section of the kidney: hilus, cortex, medulla, medullary pyramids, calyces, pelvis, and renal columns. trace the process of urine formation, identifying the areas of the nephron that are responsible for filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. trace the blood supply through the kidney and describe the changes in its composition along the way. analyze the role of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in the maintenance of water homeostasis. Skill Objectives Students will: analyze ECG result to determine normal and abnormal rhythms. measure systolic and diastolic pressure using a sphygmomanometer. perform a complete blood count using prepared blood smears. analyze a complete blood count. identify the organs forming the respiratory passageway from the nasal cavity to the alveoli of the lungs. use a spirometer to measure tidal volume, expiratory reserve volume and vital capacity. Biology Standards Cell Biology The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. Most macromolecules (polysaccharides, nucleic acids, proteins, lipids) in cells and organisms are synthesized from a small collection of simple precursors. HAP Maintenance 4
5 Physiology As a result of the coordinated structures and functions of organ systems, the internal environment of the human body remains relatively stable (homeostatic) despite changes in the outside environment. The complementary activity of major body systems provides cells with oxygen and nutrients and removes toxic waste products such as carbon dioxide. Digestion includes the secretion of stomach acid, digestive enzymes (amylases, proteases, nucleases, lipases) and bile salts into the digestion system. The kidneys have a homeostatic role in the removal of nitrogenous wastes from the blood. The liver has a homeostatic role in detoxification and keeping the blood glucose balance. Organisms have a variety of mechanisms to combat disease. Antibodies have a role in the body s response to infection. Vaccination protects an individual from infectious diseases. There are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication, the body s primary defenses against bacterial and viral infections, and effective treatments of these infections. An individual with a compromised immune system (for example, a person with AIDS) may be unable to fight off and survive infections by microorganisms that are usually benign. Phagocytes, B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes have a role in the immune system. Essential Question How are organisms structured to ensure efficiency and survival? Focus Questions How do our bodies provide oxygen and nutrients to all cells? How does blood deliver materials through the cardiovascular system? How does our body protect itself from foreign invaders? How do internal cells exchange vital gases with the environment? How can the human digestive system be viewed as a disassembly line? Where does the energy for our bodies come from? How does the urinary system function as the body s sanitation system? HAP Maintenance 5
6 UNITS of STUDY Unit 1: The Cardiovascular System Biology Standards Physiology As a result of the coordinated structures and functions of organ systems, the internal environment of the human body remains relatively stable (homeostatic) despite changes in the outside environment. The complementary activity of major body systems provides cells with oxygen and nutrients and removes toxic waste products such as carbon dioxide. Essential Question How are organisms structured to ensure efficiency and survival? Focus Questions How do our bodies provide oxygen and nutrients to all cells? Core Topics Heart valves and chambers Electric impulses in the heart Structure/function of arteries, veins and capillaries Fetal shunts Cardiac disorders Unit Objectives Students will be able to: trace the pathway of blood throughout the body as it passes through the four chambers of the human heart. identify the heart valves and describe their location, function, and mechanism of operation. trace the conduction pathway of the heart and describe the events of cardiac muscle contraction that results. outline the timing and events of the cardiac cycle (systole and diastole). compare and contrast the structure and function of arteries, veins, and capillaries. define vasoconstriction and vasodilation as they regulate blood flow into capillary beds. identify fetal vascular modifications, or fetal shunts, and describe their function before birth. distinguish cardiovascular-related disorders, including their symptoms, prevention, and control. Skill Objectives Students will: analyze ECG result to determine normal and abnormal rhythms. HAP Maintenance 6
7 measure systolic and diastolic pressure using a sphygmomanometer. Sample Assessment Parts of the circulatory system and their functions Pacing 3 weeks HAP Maintenance 7
8 Unit 2: Blood Biology Standards Physiology As a result of the coordinated structures and functions of organ systems, the internal environment of the human body remains relatively stable (homeostatic) despite changes in the outside environment. The complementary activity of major body systems provides cells with oxygen and nutrients and removes toxic waste products such as carbon dioxide. Essential Question How are organisms structured to ensure efficiency and survival? Focus Question How does blood deliver materials through the cardiovascular system? Core Topics Blood components Blood types Clotting mechanisms Blood disorders Unit Objectives Students will be able to: outline the composition, physical characteristics, and functions of whole blood. differentiate among the functions of each of the formed elements of blood and plasma. differentiate between fetal and adult hemoglobin. relate the basis for a transfusion reaction based upon ABO and Rh blood groups. outline the mechanism of blood-clotting and some factors that may affect clotting time. analyze the importance of blood testing as a diagnostic tool. identify blood-related disorders, including their symptoms, prevention, and control. Skill Objective Students will: perform a complete blood count using prepared blood smears. Sample Assessment Identify blood type and determine cross-reactions between blood types Pacing 2 weeks HAP Maintenance 8
9 Unit 3: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Biology Standards Physiology Organisms have a variety of mechanisms to combat disease. Antibodies have a role in the body s response to infection. Vaccination protects an individual from infectious diseases. There are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication, the body s primary defenses against bacterial and viral infections, and effective treatments of these infections. An individual with a compromised immune system (for example, a person with AIDS) may be unable to fight off and survive infections by microorganisms that are usually benign. Phagocytes, B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes have a role in the immune system. Essential Question How are organisms structured to ensure efficiency and survival? Focus Question How does our body protect itself from foreign invaders? Core Topics Components of the lymphatic system Immune cells Types of immunity Vaccination Unit Objectives Students will be able to: relate the function of the lymphatic system to the cardiovascular and immune systems. relate the distribution of lymph nodes and vessels to the point of entry of foreign bodies. define the composition of lymph and explain its formation and transport through lymph nodes and lymph organs. summarize the body s three lines of defense against pathogens compare and contrast the development and function of T-lymphocytes and B- lymphocytes. analyze the structure of an antibody in terms of genetic recombination. distinguish between active and passive immunity as well as between natural and artificial immunity. HAP Maintenance 9
10 compare immunodeficiencies, allergies, and autoimmune diseases. Skill Objective Students will: analyze a complete blood count. Sample Assessment Genetics of antibody diversity Pacing 2.5 weeks HAP Maintenance 10
11 Unit 4: The Respiratory System Biology Standards Physiology As a result of the coordinated structures and functions of organ systems, the internal environment of the human body remains relatively stable (homeostatic) despite changes in the outside environment. The complementary activity of major body systems provides cells with oxygen and nutrients and removes toxic waste products such as carbon dioxide. Essential Question How are organisms structured to ensure efficiency and survival? Focus Question How do internal cells exchange vital gases with the environment? Core Topics Respiratory organ structure and function Types of respiration Pressure/volume relationships in breathing Gas transport Respiratory disorders Unit Objectives Students will be able to: define the structure and function of each respiratory organ. differentiate among cellular respiration, external respiration, internal respiration, pulmonary ventilation, expiration, and inspiration. trace how the respiratory muscles can cause volume changes that lead to air flow into and out of the lungs. summarize the process of gas exchanges in the lungs and tissues by applying the gas laws. compare and contrast how oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the blood. compare the causes and consequences of chronic bronchitis, emphysema, asthma, and lung cancer. Skill Objectives Students will: identify the organs forming the respiratory passageway from the nasal cavity to the alveoli of the lungs. use a spirometer to measure tidal volume, expiratory reserve volume and vital capacity. Sample Assessment HAP Maintenance 11
12 Role of carbon dioxide Pacing 2 weeks HAP Maintenance 12
13 Unit 5: The Digestive System Biology Standards Physiology As a result of the coordinated structures and functions of organ systems, the internal environment of the human body remains relatively stable (homeostatic) despite changes in the outside environment. Digestion includes the secretion of stomach acid, digestive enzymes (amylases, proteases, nucleases, lipases) and bile salts into the digestion system. The liver has a homeostatic role in detoxification and keeping the blood glucose balance. Essential Question How are organisms structured to ensure efficiency and survival? Focus Question How can the human digestive system be viewed as a disassembly line? Core Topics Digestive system components Mechanical vs. chemical digestion Digestive juices Digestive disorders Unit Objectives Students will be able to: summarize the overall function of the digestive system and differentiate between organs of the alimentary canal and accessory digestive organs. differentiate between mechanical/physical digestion and chemical digestion and where each process occurs in the alimentary canal. outline the general activities of each digestive system organ. differentiate between deciduous and permanent teeth outline the mechanisms of chewing, swallowing, choking, peristalsis, absorption, vomiting, and defecation. define the composition, origin, and activity of each of the major digestive juices. define the function of the villus in normal and abnormal digestive processes. identify digestion-related disorders, including their symptoms, prevention, and control. Sample Assessment Enzymatic breakdown of nutrients Pacing 2.5 weeks HAP Maintenance 13
14 Unit 6: Nutrition and Metabolism Biology Standards Cell Biology The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism s cells. Most macromolecules (polysaccharides, nucleic acids, proteins, lipids) in cells and organisms are synthesized from a small collection of simple precursors. Essential Question How are organisms structured to ensure efficiency and survival? Focus Question Where does the energy for our bodies come from? Core Topics Major nutrient types BMR Building blocks of protein synthesis Unit Objectives Students will be able to: identify the six major nutrient categories, noting the important dietary sources, energy content, and principle cellular uses of each. define enzyme, metabolism, anabolism, and catabolism. analyze the importance of energy balance and basal metabolic rate (BMR) Distinguish between fat- and water-soluble vitamins and describe consequences of their deficit or excess. summarize the need for protein synthesis in body cells and the supply of dietary amino acids from complete and incomplete proteins. compare and contrast saturated and unsaturated fatty acids and the consequences of their deficit or excess. differentiate between LDLs and HDLs relative to their structures and major roles in the body. Skill Objective Students will: compare their personal nutritional needs with their actual nutritional intake. Sample Assessment Food nutrients testing Pacing 2 weeks HAP Maintenance 14
15 Unit 7: Excretory System Biology Standards Physiology As a result of the coordinated structures and functions of organ systems, the internal environment of the human body remains relatively stable (homeostatic) despite changes in the outside environment. The kidneys have a homeostatic role in the removal of nitrogenous wastes from the blood. Essential Question How are organisms structured to ensure efficiency and survival? Focus Question How does the urinary system function as the body s sanitation system? Core Topics Kidney structure Waste removal through urine formation Water homeostasis Unit Objectives Students will be able to: identify the following regions of a longitudinal section of the kidney: hilus, cortex, medulla, medullary pyramids, calyces, pelvis, and renal columns. trace the process of urine formation, identifying the areas of the nephron that are responsible for filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. trace the blood supply through the kidney and describe the changes in its composition along the way. analyze the role of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in the maintenance of water homeostasis. Skill Objectives Students will: illustrate the gross anatomy of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. diagnose normal and abnormal simulated urine samples. Sample Assessment Urinalysis lab Pacing 1 week HAP Maintenance 15
16 Unit 8: CPR and AED Training (optional unit based on teacher certification through Red Cross) Students may be offered the opportunity to attain certification through the American Red Cross in CPR if the teacher is a certified Red Cross Instructor. Pacing 1 week HAP Maintenance 16
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
Anatomy and Physiology UNIT I: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology The student will demonstrate an understanding of the anatomic and physiological basis of life and the ability to explain the interdependence
2161-1 - Page 1. Name: 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. Questions 10 and 11 refer to the following:
 Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Name: 2161-1 - Page 1 1) Choose the disease that is most closely related to the given phrase. a disease of the bone marrow characterized by uncontrolled production of white blood cells A) meningitis B)
Chapter 48. Nutrients in Food. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids. Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids, continued
 Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Lipids The three nutrients needed by the body in the greatest amounts are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Nutrients in Food All of these nutrients are called organic compounds,
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide
 Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
Paramedic Program Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Define the terms anatomy and physiology. List and discuss in order of increasing complexity, the body from the cell to the whole organism. Define the
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES
 BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
BIO 137: CHAPTER 1 OBJECTIVES 1. Define the terms anatomy and physiology, and explain their relationship using an example of a human structure with its corresponding function. A. ANATOMY = the study of
37 2 Blood and the Lymphatic System Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
1 of 34 Blood is a connective tissue that contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells. 2 of 34 The functions of blood include: collecting oxygen from the lungs, nutrients from the digestive
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II (BIO 2312) SYLLABUS
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II (BIO 2312) SYLLABUS NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY The City University Of New York School of Arts and Sciences Department of Biological Sciences Course Information Course
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II (BIO 2312) SYLLABUS NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY The City University Of New York School of Arts and Sciences Department of Biological Sciences Course Information Course
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information
 201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
201 Webster Building 3411 Silverside Road Wilmington, DE 19810 Phone: 1-888-658-6641 Fax: 1-302-477-9744 learn@corexcel.com www.corexcel.com Course Outline, Objectives and Accreditation Information Chapter
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX
 OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
OUTCOMES BASED LEARNING MATRIX Course: BIOL 206 Vertebrate Anatomy and Physiology II Department: Biology Course Description: This is the second part of an introductory course sequence in the comparative
Introduction to Animal Systems
 Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
Human Body Systems Introduction to Animal Systems Recurring Themes in Biology 1. Correlation between structure and function( seen at many levels) 2. Life is organized at many levels from Smallest ----
The Respiratory System
 Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Human Anatomy III: Respiratory, Urinary & Digestive Systems The Respiratory System Major functions include: Obtaining oxygen Removing carbon dioxide Maintenance of ph balance Respiration may be accomplished
Functions of Blood. Collects O 2 from lungs, nutrients from digestive tract, and waste products from tissues Helps maintain homeostasis
 Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Blood Objectives Describe the functions of blood Describe blood plasma Explain the functions of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets Summarize the process of blood clotting What is Blood?
Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus
 Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus When Key Points / Objectives Content Day 1 INTRODUCTION HOMEOSTASIS LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION Day 2 CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GENETICS Day 3 INTEGUMENTARY
Anatomy and Physiology (ANPY) CTY Course Syllabus When Key Points / Objectives Content Day 1 INTRODUCTION HOMEOSTASIS LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION Day 2 CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GENETICS Day 3 INTEGUMENTARY
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School
 Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Chetek-Weyerhaeuser High School Anatomy and Physiology Units and Anatomy and Physiology A Unit 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology (6 days) Essential Question: How do the systems of the human
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan
 Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Human Body Systems Project By Eva McLanahan Students will work in groups to research one of the eleven body systems as found in Holt, Rinehart, and Winston Modern Biology (2002). Research will focus on
Anatomy and Physiology
 Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
Learning Activities It is important that you do not lecture all of the time. If you employ a variety of teaching styles, your students will stay focused better and they will find it easier to process the
THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS
 Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
Name Period Date THE HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS System Function Diagram Major Organs Digestive 1. take in food (ingestion) 2. digest food into smaller molecules and absorb nutrients 3. remove undigestable food
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
ORGAN SYSTEMS OF THE BODY DEFINITIONS AND CONCEPTS A. Organ a structure made up of two or more kinds of tissues organized in such a way that they can together perform a more complex function that can any
CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE VETERINARY SCIENCE ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE VETERINARY SCIENCE ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Course Number 5407 Department Agriculture Length of Course Two (2) Semesters/One (1) year Grade Level
CHINO VALLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL GUIDE VETERINARY SCIENCE ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Course Number 5407 Department Agriculture Length of Course Two (2) Semesters/One (1) year Grade Level
North Bergen School District Benchmarks
 Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Grade: 10,11, and 12 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology First Marking Period Define anatomy and physiology, and describe various subspecialties of each discipline. Describe the five basic functions of living
Lecture Time: Online + Saturdays June 13 th to August 8 th from 1PM to 3PM Lab Time: Saturdays June 13 th to August 8 th from 3PM to 5PM:
 BIOL 170: Human Physiology Instructor: Jerome Garcia Lecture Time: Online + Saturdays June 13 th to August 8 th from 1PM to 3PM Lab Time: Saturdays June 13 th to August 8 th from 3PM to 5PM: Course Syllabus
BIOL 170: Human Physiology Instructor: Jerome Garcia Lecture Time: Online + Saturdays June 13 th to August 8 th from 1PM to 3PM Lab Time: Saturdays June 13 th to August 8 th from 3PM to 5PM: Course Syllabus
Digestive System Notes
 Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Digestive System Notes Structure Function Relation Mouth cavity Mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva. Salivary glands Three pairs of glands which secrete saliva containing
Course of Study. Anatomy & Physiology. Warren County Career Center. 3525 North State Route 48 Lebanon, Ohio 45036. Adopted 6-15-06
 Course of Study Anatomy & Physiology Warren County Career Center 3525 North State Route 48 Lebanon, Ohio 45036 Adopted 6-15-06 This document is for the use of the staff at Warren County Career Center.
Course of Study Anatomy & Physiology Warren County Career Center 3525 North State Route 48 Lebanon, Ohio 45036 Adopted 6-15-06 This document is for the use of the staff at Warren County Career Center.
Functions of Blood System. Blood Cells
 Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Functions of Blood System Transport: to and from tissue cells Nutrients to cells: amino acids, glucose, vitamins, minerals, lipids (as lipoproteins). Oxygen: by red blood corpuscles (oxyhaemoglobin - 4
Eating, pooping, and peeing THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Ingested food is not technically in the body until it is absorbed so it needs to be: Mechanically and chemically reduced Transported by the blood to the cells Large portions are not
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 th Edition, 2015 Marieb
 A Correlation of Essentials of Human Anatomy Marieb To the Next Generation Science Standards Life A Correlation of, HS-LS1 From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes HS-LS1-1. Construct an explanation
A Correlation of Essentials of Human Anatomy Marieb To the Next Generation Science Standards Life A Correlation of, HS-LS1 From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes HS-LS1-1. Construct an explanation
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Chapter 15. The Urinary System. Slides 15.1 15.20. Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L.
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 15 The Urinary System Slides 15.1 15.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Functions of the Urinary System Elimination
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 15 The Urinary System Slides 15.1 15.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Functions of the Urinary System Elimination
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411
 10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
10.2 The Human Digestive System pg. 411 The human digestive system is made up of a group of organs working together. The digestive tract is made up of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and
The digestive system eliminated waste from the digestive tract. But we also need a way to eliminate waste from the rest of the body.
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system 1
Ranger College Syllabus
 Ranger College Syllabus Course number and title: Biology 2402 Anatomy and Physiology II Credit Hours: 4 hours/week (lecture 4 hours/week, lab 3 hours/week) Name of Instructor (title): Gretchin Geye Office
Ranger College Syllabus Course number and title: Biology 2402 Anatomy and Physiology II Credit Hours: 4 hours/week (lecture 4 hours/week, lab 3 hours/week) Name of Instructor (title): Gretchin Geye Office
The Circulatory System. Chapter 17 Lesson 1
 The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
The Circulatory System Chapter 17 Lesson 1 Functions of the Circulatory System Your circulatory system maintains an internal environment in which all the cells in your body are nourished. As your heart
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Section 1 (The Body s Transport System) Chapter 16: Circulation 7 th Grade Cardiovascular system (the circulatory system) includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood carries needed substances to the cells
Human Anatomy & Physiology General
 Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
Human Anatomy & Physiology General Biology is the study of life but, what exactly is life? how are living things different from nonliving things eg. a human from a rock eg. a a human from a robot eg. a
UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM
 BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
BIOLOGY - 2201 UNIT 3 : MAINTAINING DYNAMIC EQUILIBRIUM What happens to your body as you run? Breathing, heart rate, temperature, muscle pain, thirsty... Homeotasis Homeostasis is the process of maintaining
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition
 Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
Topic 4: Digestion and Nutrition THE CONTENTS OF FOOD Food contains nutrients: Nutrients include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nutrients must be small enough to enter our cells. If they are too large they must be digested
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
33.1 The Circulatory System
 33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
33.1 The Circulatory System Lesson Objectives Identify the functions of the human circulatory system. Describe the structure of the heart and explain how it pumps blood through the body. Name three types
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford
 By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
By Casey Schmidt and Wendy Ford Body systems Digestive System Circulatory System Respiratory System Excretory System Immune System Reproductive System Nervous System Muscular System Skeletal System Endocrine
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST
 REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
REVIEW for BIOLOGY UNIT TEST NOTE: The Unit Test will cover everything we have learned in the Biology Unit, starting from cell structures, cell division, various organ systems, disorders, organ donation,
Anatomy/Physiology Course Summary Department: Science. Semester 1
 Anatomy/Physiology Course Summary Department: Science Semester 1 Learning Objective #1 Students will be able to understand and use the language of the discipline in addition to understanding the concept
Anatomy/Physiology Course Summary Department: Science Semester 1 Learning Objective #1 Students will be able to understand and use the language of the discipline in addition to understanding the concept
Pre-requisites: Successful completion of 4th grade science and the 4th grade science assessment.
 Throughout each unit, assessments are incorporated into lessons. These assessments are activities that occur within the context of each lesson providing the guidelines for assessing students' progress.
Throughout each unit, assessments are incorporated into lessons. These assessments are activities that occur within the context of each lesson providing the guidelines for assessing students' progress.
Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases
 Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases 1/9/2015 Renal Biology - Sandra Hsu 1 Renal Functions 1) excrete metabolic wastes (blood cleaning)
Renal Topics 1) renal function 2) renal system 3) urine formation 4) urine & urination 5) renal diseases 1/9/2015 Renal Biology - Sandra Hsu 1 Renal Functions 1) excrete metabolic wastes (blood cleaning)
5. Secretion: release of water, acids. Enzymes, buffers by digestive tract.
 Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Digestive System CH-16 Lecture topics Functions of the digestive system: p. 488. 1. Ingestion: Taking food in 2. Propulsion: movement of food thru alimentary canal p.490. voluntary: swalloing : skeletal
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. 7 th edition Marieb, Elaine, 2003. Chapters 10-11. Lab Manual, 2 nd edition and coloring book, 7 th edition
 Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
Topic/Unit: Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System Curricular Goals/ Learning Outcomes: Students will be able to identify the composition of blood and its function. Students will be able to differentiate
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY MODULE 2015/16
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY MODULE 2015/16 STUDENT INFORMATION MODULE CO-ORDINATOR: Email: edged@tcd.ie DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY, BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES INSTITUTE, TRINITY COLLEGE, PEARSE STREET, DUBLIN 2. Module
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY MODULE 2015/16 STUDENT INFORMATION MODULE CO-ORDINATOR: Email: edged@tcd.ie DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY, BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES INSTITUTE, TRINITY COLLEGE, PEARSE STREET, DUBLIN 2. Module
1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood?
 1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
1 1 The diagram shows blood as seen under a microscope. Which identifies parts P, Q, R and S of the blood? 2 The plan shows the blood system of a mammal. What does the part labelled X represent? A heart
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Circulatory System Review 1. Draw a table to describe the similarities and differences between arteries and veins? Anatomy Direction of blood flow: Oxygen concentration: Arteries Thick, elastic smooth
Bio 348 Human Anatomy & Physiology Lapsansky 2014
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES NOTE: Please review the objectives for both the lecture and lab in preparation for lecture exams. Although lab questions will not be on the lecture exams, many of the objectives overlap,
LEARNING OBJECTIVES NOTE: Please review the objectives for both the lecture and lab in preparation for lecture exams. Although lab questions will not be on the lecture exams, many of the objectives overlap,
Chapter 17 Digestive System. Alimentary Canal. Movements of the Tube
 Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Chapter 17 Digestive System Functions of Digestive System ingestion mechanical digestion chemical digestion propulsion absorption defecation Consists of the alimentary canal and accessory organs 1 Alimentary
Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System
 The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
The Digestive System Magic School Bus Digestive System Brainpop Digestive System 1 Functions of the Digestive System: 1. Break up food into smaller pieces 2. Absorbing nutrients into the blood 3. Excreting
Respiration occurs in the mitochondria in cells.
 B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
B3 Question Which process occurs in the mitochondria in cells? Why do the liver and muscle cells have large number of mitochondria? What is the function of the ribosomes? Answer Respiration occurs in the
Get It Right. Answers. Chapter 1: The Science of Life. A biologist studies all living things.
 Discover Biology 'N' Level Science Chapter 1 Chapter 1: The Science of Life A biologist studies all living things. In order to carry out the scientific method, we need to ask questions. Discover Biology
Discover Biology 'N' Level Science Chapter 1 Chapter 1: The Science of Life A biologist studies all living things. In order to carry out the scientific method, we need to ask questions. Discover Biology
H.W. 1 Bio 101 Prof. Fournier
 H.W. 1 Bio 101 Prof. Fournier 1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a
H.W. 1 Bio 101 Prof. Fournier 1. What is a similarity between all bacteria and plants? A) They both have a nucleus B) They are both composed of cells C) They both have chloroplasts D) They both lack a
Unit I: Introduction To Scientific Processes
 Unit I: Introduction To Scientific Processes This unit is an introduction to the scientific process. This unit consists of a laboratory exercise where students go through the QPOE2 process step by step
Unit I: Introduction To Scientific Processes This unit is an introduction to the scientific process. This unit consists of a laboratory exercise where students go through the QPOE2 process step by step
GRADE 11F: Biology 3. UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours. Human gas exchange system and health. Resources. About this unit. Previous learning.
 GRADE 11F: Biology 3 Human gas exchange system and health UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours About this unit This unit is the third of six units on biology for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your
GRADE 11F: Biology 3 Human gas exchange system and health UNIT 11FB.3 9 hours About this unit This unit is the third of six units on biology for Grade 11 foundation. The unit is designed to guide your
Human Biological Science 2
 SUBJECT OUTLINE Subject Name: Human Biological Science 2 SECTION 1 GENERAL INFORMATION Subject Code: BIOH122 Award/s: Total course credit points: Level: Bachelor of Health Science (Naturopathy) 128 1 st
SUBJECT OUTLINE Subject Name: Human Biological Science 2 SECTION 1 GENERAL INFORMATION Subject Code: BIOH122 Award/s: Total course credit points: Level: Bachelor of Health Science (Naturopathy) 128 1 st
Outline Digestive System
 Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Outline Digestive System The Digestive System Digestive System Lecture Packet 19 Chapter 15 I. Function II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,
Chapter 19 Ci C r i cula l t a i t o i n
 Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
Chapter 19 Circulation A closed system Circulatory System Consisting of Heart, Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, Blood & the Lymphatic system Blood Make up The blood is made up of Plasma and three main types
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402
 10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
10.1 The function of Digestion pg. 402 Macromolecules and Living Systems The body is made up of more than 60 % water. The water is found in the cells cytoplasm, the interstitial fluid and the blood (5
A: Nursing Knowledge. Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 1
 A: Nursing Knowledge Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 1 Competency: A-1 Anatomy and Physiology A-1-1 A-1-2 A-1-3 A-1-4 A-1-5 A-1-6 A-1-7 A-1-8 Identify the normal structures and functions
A: Nursing Knowledge Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 1 Competency: A-1 Anatomy and Physiology A-1-1 A-1-2 A-1-3 A-1-4 A-1-5 A-1-6 A-1-7 A-1-8 Identify the normal structures and functions
1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption?
 Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestion Review 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The
Digestion, Absorption. How & where?
 Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
Digestion, Absorption How & where? What happens to food? Three processes Digestion Absorption Elimination Where do they occur? GI tract Overview of Digestion GI tract Gastrointestinal (GI) tract: series
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
CHAPTER 1: THE LUNGS AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION Lung cancer affects a life-sustaining system of the body, the respiratory system. The respiratory system is responsible for one of the essential
1. The diagram below represents a biological process
 1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
1. The diagram below represents a biological process 5. The chart below indicates the elements contained in four different molecules and the number of atoms of each element in those molecules. Which set
BLOOD-Chp. Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? What is the composition of blood? 3 major types of plasma proteins
 6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
6.1 Blood: An overview BLOOD-Chp Chp.. 6 What are the functions of blood? Transportation: oxygen, nutrients, wastes, carbon dioxide and hormones Defense: against invasion by pathogens Regulatory functions:
Digestive System. Gross Anatomy and Physiology
 Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
Digestive System Gross Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. Base Function: Working with the circulatory system the digestive system provides the body with fuel. B. Main players: 1. Digestive tract:
10. T and B cells are types of a. endocrine cells. c. lymphocytes. b. platelets. d. complement cells.
 Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
Virus and Immune System Review Directions: Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. 1. Why does a cut in the skin threaten the body s nonspecific defenses against disease? a. If a cut bleeds, disease-fighting
30.3 The Digestive System
 30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
30.3 The Digestive System Lesson Objectives Describe the organs of the digestive system and explain their functions. Explain what happens during digestion. Describe how nutrients are absorbed into the
Get Your Students Excited About Anatomy/Physiology. Julie Combes, B.S., M.ED Lamesa High School Lamesa, Texas jcombes@lamesaisd..
 Get Your Students Excited About Anatomy/Physiology Julie Combes, B.S., M.ED Lamesa High School Lamesa, Texas jcombes@lamesaisd..net Disclamer I am not promoting any one product or company. When I mention
Get Your Students Excited About Anatomy/Physiology Julie Combes, B.S., M.ED Lamesa High School Lamesa, Texas jcombes@lamesaisd..net Disclamer I am not promoting any one product or company. When I mention
CHAPTER 20: URINARY SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal.
OBJECTIVES: 1. Name the major function of the urinary system, and name and locate (on a diagram) the organs that compose the system. 2. Explain what the term renal refers to. 3. Define the term retroperitoneal.
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal
 Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Regulating the Internal Environment Water Balance & Nitrogenous Waste Removal 2006-2007 Animal systems evolved to support multicellular life CH CHO O 2 O 2 NH 3 CH CHO O 2 CO 2 NH NH 3 O 2 3 NH 3 intracellular
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture. Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1
 Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
Anatomy & Physiology Bio 2401 Lecture Instructor: Daryl Beatty Day 1 Intro to Lecture 1 Introduction: Daryl Beatty M.S. Microbiology 28 Years Dow, Research & TS&D. Family BC since 2007 More importantly:
Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237)
 Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237) Functions: Transports Excess Interstitial Fluid Back to Bloodstream Lymphatic vessels collect lymph from loose
Unit 9: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NURSING PHYSIOLOGY (NRSG237) Functions: Transports Excess Interstitial Fluid Back to Bloodstream Lymphatic vessels collect lymph from loose
Digestion. What we ll cover. Main stages of digestion. Digestion: A Closer Look. A Tour of the Human Digestive System. Mechanical digestion
 Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
Digestion What we ll cover What are the digestive system structures and their functions? Where does carbohydrate, protein and fat digestion and absorption occur? What are the 3 accessory organs of digestion?
The chemical reactions inside cells are controlled by enzymes. Cells may be specialised to carry out a particular function.
 12.1 What are animals and plants built from? All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. to relate the structure of different types
12.1 What are animals and plants built from? All living things are made up of cells. The structures of different types of cells are related to their functions. to relate the structure of different types
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478
 12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
12.1: The Function of Circulation page 478 Key Terms: Circulatory system, heart, blood vessel, blood, open circulatory system, closed circulatory system, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, aorta, atrioventricular
Engage: Brainstorming Body Systems. Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below.
 Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Engage: Brainstorming Body s Record the structures and function of each body system in the table below. Body Nervous Circulatory Excretory Immune Digestive Respiratory Skeletal Muscular Endocrine Integumentary
Digestive System Functions
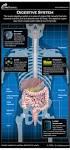 Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Digestive System Functions A. Gastrointestinal Processes 1. Ingestion: placing food in mouth (voluntary) 2. Propulsion: moving food through GI tract a. Peristalsis: alternating waves of contraction and
Urinary System. And Adrenal Function
 Urinary System And Adrenal Function Overview Kidney anatomy and physiology Urine Ureters, Bladder and Urethra Adrenal Function Functions of the Kidney Filter fluids from the blood Regulate volume and composition
Urinary System And Adrenal Function Overview Kidney anatomy and physiology Urine Ureters, Bladder and Urethra Adrenal Function Functions of the Kidney Filter fluids from the blood Regulate volume and composition
LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION
 LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION Components of the Urinary System 2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Bladder Urethra Refer to Renal System Vocabulary in your notes Figure 2-1,page10 Kidney Composition Cortex Outer region Contains
LECTURE 1 RENAL FUNCTION Components of the Urinary System 2 Kidneys 2 Ureters Bladder Urethra Refer to Renal System Vocabulary in your notes Figure 2-1,page10 Kidney Composition Cortex Outer region Contains
The Digestive System. You are what you eat!
 The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
The Digestive System You are what you eat! Try to label the diagram (PENCIL!!) What is Digestion? Digestion: the breakdown of large macromolecules (proteins, fats, carbohydrates) into smaller molecules
Nerve Tissue. Muscle Tissue. Connective Tissue
 Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Human Body Tissues Levels of Organization 1. Cells 2. = groups of similar cells that perform a 3. Organ = 4. = group of organs Four Major Tissues 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissue Nerve Tissue Muscle Tissue
Liver Function Essay
 Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Liver Function Essay Name: Quindoline Ntui Date: April 20, 2009 Professor: Dr. Danil Hammoudi Class: Anatomy and Physiology 2 Liver function The human body consist of many highly organize part working
Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi
 Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
Lec.13 Medical Physiology Z.H.Al-Zubaydi Functions of the Digestive System The major functions of the digestive tract include the following six processes, summarized in Figure 1: 1. Ingestion Food must
The Excretory and Digestive Systems
 The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
The Excretory and Digestive Systems 38.2 The Process of Digestion Organs of the Digestive System The digestive system includes the: Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small and large intestine. Other structures
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA
 Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
Overview... 1 What is the Outreach Program?... 1 Concepts... 2 Objectives... 3 Arizona Science Standards... 3 College and Career Ready ELA Standards... 4 Next Generation Science Standards... 4 Learning
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab
 BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOL 1108 Vertebrate Anatomy Lab This lab explores major organs associated with the circulatory, excretory, and nervous systems of mammals. Circulatory System Vertebrates are among the organisms that have
BIOLOGY HIGHER LEVEL
 2008. M44 Write your Examination Number here Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2008 BIOLOGY HIGHER LEVEL THURSDAY, 12 JUNE MORNING, 9.30 TO 12.30
2008. M44 Write your Examination Number here Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2008 BIOLOGY HIGHER LEVEL THURSDAY, 12 JUNE MORNING, 9.30 TO 12.30
2) Digestion the breakdown of. There are two types of digestion: Mechanical and Chemical. 3) Absorption when the nutrients enter into the blood.
 The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
The Digestive System Video on the digestive system (5 min) The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown of the we eat so that it can be absorbed into the. There are four main stages of the digestive
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system
 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system 2.06 Understand the functions and disorders of the respiratory system Essential questions What are the functions of the respiratory
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES. 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions.
 KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
KEY CHAPTER 14: BLOOD OBJECTIVES 1. Describe blood according to its tissue type and major functions. TISSUE TYPE? MAJOR FUNCTIONS connective Transport Maintenance of body temperature 2. Define the term
Blood Transfusion. Red Blood Cells White Blood Cells Platelets
 Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions are very common. Each year, almost 5 million Americans need a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions are given to replace blood lost during surgery or serious
Blood Transfusion Introduction Blood transfusions are very common. Each year, almost 5 million Americans need a blood transfusion. Blood transfusions are given to replace blood lost during surgery or serious
1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled B on the diagram.
 2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
2013 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled A on the diagram. 2. Give the name and functions
Diabetes and Your Circulatory System: The story of the lost limbs.
 Diabetes and Your Circulatory System: The story of the lost limbs. Dr. Falak Almiladi William H Brown Math and Science Academy IIT Research Mentor: Dr. Eric Brey This material is based upon work supported
Diabetes and Your Circulatory System: The story of the lost limbs. Dr. Falak Almiladi William H Brown Math and Science Academy IIT Research Mentor: Dr. Eric Brey This material is based upon work supported
Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems
 Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems The Importance of Homeostasis The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment, i.e., homeostasis, is essential for life. Cellular conditions that need
Chapter 20: Tissues & Organ Systems The Importance of Homeostasis The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment, i.e., homeostasis, is essential for life. Cellular conditions that need
Blood vessels. transport blood throughout the body
 Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
Circulatory System Parts and Organs Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body Arteries blood vessels that carry blood AWAY from the heart Pulmonary arteries carry the deoxygenated blood from heart
CORE MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Course Syllabus
 Course Syllabus Course Number: HLTH-0342 OHLAP Credit: No OCAS Code: None Course Length: 45 Hours Career Cluster: Health Science Career Pathway: Therapeutic Services Career Major(s): Pre-requisite(s):
Course Syllabus Course Number: HLTH-0342 OHLAP Credit: No OCAS Code: None Course Length: 45 Hours Career Cluster: Health Science Career Pathway: Therapeutic Services Career Major(s): Pre-requisite(s):
The Body s Transport System
 Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Circulation Name Date Class The Body s Transport System This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology John Wojciakowski email: jwojciakowski@nvps.net phone ext: 28351 Room #1245 TEXTS: Text The Human Body Book author- Steve Parker copyright- 2007 Course Overview: Anatomy is a
Human Anatomy & Physiology John Wojciakowski email: jwojciakowski@nvps.net phone ext: 28351 Room #1245 TEXTS: Text The Human Body Book author- Steve Parker copyright- 2007 Course Overview: Anatomy is a
